Automatic streetlight control and fault detection for smart, flexible and responsible cities

When you say automatic street lighting operation, the first thing that probably comes to your mind is a system that is working by itself, with no intervention from a human. Even if you are not too far from the truth, the real question is why would a city need such a system?
Streetlights. They are so widespread that they go unnoticed by most of us. The only thing that we know for sure about streetlights is that during the night, they light up the streets without interruption and throughout the daytime they are unused. However, the traditional lighting system that we all are used to comes with limitations: manually switching lights On/Off, the lack of segmented operation, high operational costs, relying on residents for spotting grid malfunctions and delayed repairs. Automatic streetlight control is a simple, yet powerful concept that overcomes all these limitations.
Today, in a bid to shape cities’ development and the people’s experiences as a whole, cities are starting to see the reason why embracing automatic streetlight systems might prove a viable option for achieving their efficiency and sustainability goals. That’s mainly because, among all innovative applications, streetlights play a vital role in our environment and go beyond the functional aspects. While it is an element necessary for visibility and security, it also brings new possibilities for developing and rethinking the city nightscape and the way citizens interact with the urban environment.
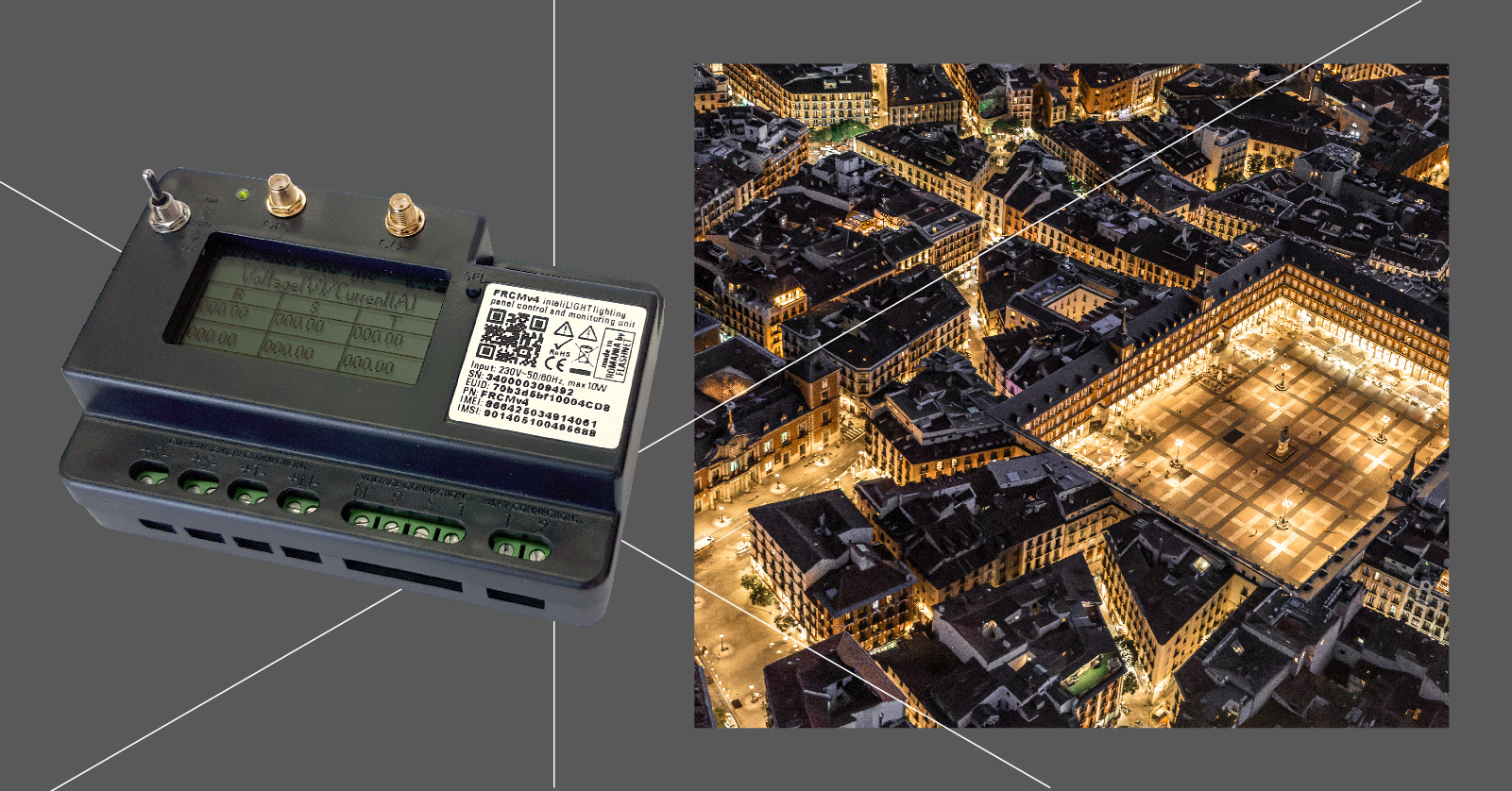
Countries like Spain, Greece and Belgium have already made a few steps in that direction by implementing the inteliLIGHT smart street lighting system that provides three levels of automation: autonomous street lighting operation , automatic fault detection and automatic maintenance teams deployment. It seems clear that all cities aspire to have a lighting infrastructure that is flexible, reliable and fast responding, while avoiding energy loss. But what makes an automatic streetlight system an optimum solution for cities that embrace innovation and how does it work in practice?
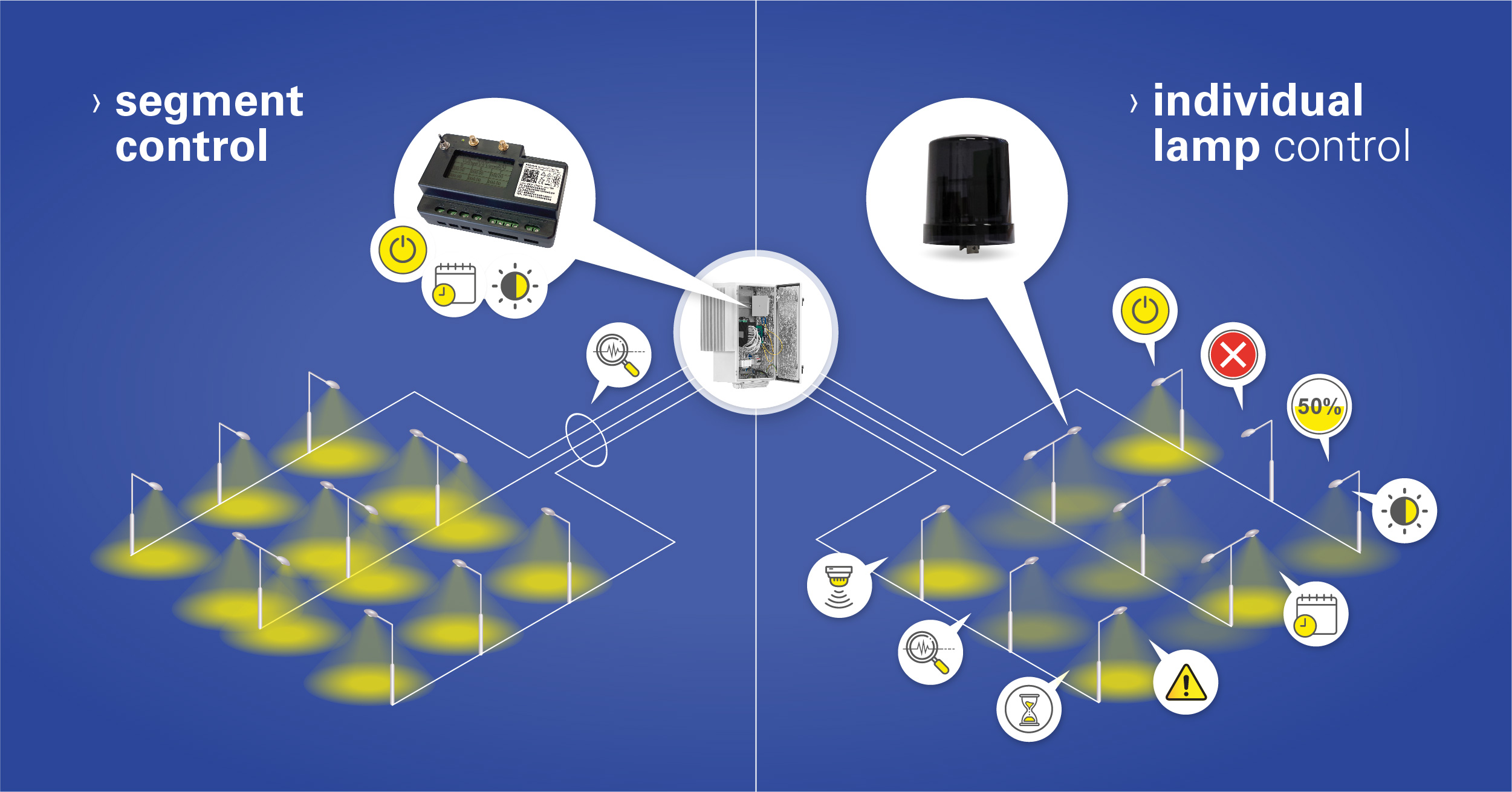
Autonomous street lighting operation
Time
One of the most common ways for automating streetlights is according to the time of the day. This means that a certain hour could be set for the lights to be automatically switched on when it starts getting dark (an essential need especially in winter months), and then can be scheduled to automatically dim down later in the night during off-peak hours when there are fewer people on the streets and open spaces. Imagine your city hosting a night festival that is taking over the course of 5 days. In this case, the light could be set to dim up progressively as the starting hour of the event approaching and be automatically switched off after the event has ended.
Light Sensors
Sun tracking sensors? This means controlling the streetlighting depending on the outside lighting conditions. In the case of thick mist, a solar eclipse or dark clouds that bring a storm, by using sensors, the automatic street lighting system enhances public safety by adjusting the light output in the needed areas. Besides providing a safe space for communities at all times, the automatic system plays an important role in reducing operating costs and the usage of resources. It also addresses the problem of unnecessary or excessive light which could become an issue from the perspective of light pollution.
Motion Sensors
A motion sensor installed in the lighting source automatically activates when a car or pedestrian is noticed in the area, enabling adaptive lighting. If the sensors do not record any activity, the lights are then automatically adjusted to the most optimal light level. It ensures there isn’t any energy used in empty places that don’t need lighting, without sacrificing the safety of the traffic participants.
More than that, this is important in terms of sustainability, as it ensures there isn’t any energy used in empty places that don’t need lighting. So, it would be fair to say that an automatic street lighting system could be considered a catalyst for energy and cost savings.
Automatic fault detection
Generally, the faults of the lighting grid are taking days (even months) to be repaired by the staff that goes on regular “patrols” with the mission to check faulty lamps. They also rely on the community of people to notice and report any dysfunction of streetlights.
Switching to an automatic streetlighting system that detects fault eliminates any wasted time and error in detecting and reporting malfunctions. Whenever a fault occurs along the grid, it is automatically detected by sensors and automatically a problem in just a few seconds. As the technicians will know the exact location of the faulty light, the time needed for searching and repairing the fault is hence reduced and up to 42% maintenance costs are saved.
This automatic street lighting maintenance could at the same time make it easier for municipalities to expand the street lighting system to additional areas and increase the availability of streetlight in underserved areas. More than that, the fast detection and repair of faulty lights improve safety conditions for both vehicles and pedestrians are highly improved.
Automation for smart cities
So what’s next? Due to the lamp-level control, the street light networks are continuously under power. Therefore, there is an array of solutions that can already be deployed together with the modern automatic street lighting system by mounting sensors and applications on the lighting network. Security cameras, communication antennas, pollution sensors, noise detectors or traffic density sensors are just a few examples. By connecting every lighting pole to a wider network connection, each lamp becomes an IoT-ready installation platform which will act as a binder for wider smart city investments.